Electricity, the unseen force that powers our modern world, is a remarkable phenomenon that has transformed every aspect of our lives. From lighting up our homes to driving technological advancements, understanding electricity is essential to appreciating how it influences our daily routines and global systems. This fundamental force enables us to communicate across continents, operate complex machinery, and enjoy the convenience of countless electronic devices. Yet, despite its ubiquitous presence, many of us are still intrigued by the inner workings and mysteries of electricity.
At Miracle Learning Centre, we understand the importance of grasping the principles behind electricity. In Singapore our experienced tutors are dedicated to providing comprehensive science tuition. Through interactive teaching methods and a passion for scientific exploration, we strive to empower students and equip them with a solid foundation in electricity and beyond.
Come along on an electrifying journey as we unravel the secrets of electricity, from its creation and generation to its various types and practical uses. Let’s explore the fascinating world of electricity and learn about all the wonders it can do.
What is Electricity?
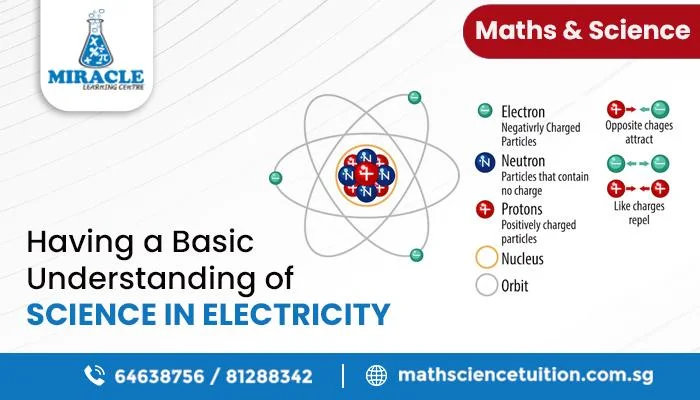
Our modern world is propelled by the strong force of electricity, which gives us access to heat, light, and the capacity to power a wide variety of appliances. Electricity is fundamentally the flow of an electric charge through a conductor. It is a kind of energy that may take on many different forms, including light, heat, electrical current, and static electricity.
Electricity is produced by electrons and other subatomic particles carrying electric charge. The velocity of these charged particles causes the production of electricity. The fact that electricity is a phenomena that we can harness and use in numerous ways rather than a material is crucial to keep in mind.
Understanding the principles behind electricity allows us to tap into its immense potential and benefit from its applications in our everyday lives. From powering our homes to fuelling technological advancements, electricity is a fundamental force that has revolutionized the way we live.
How is electricity created?
Electricity is generated through various methods, each harnessing different sources of energy. Let’s explore some of the key techniques and processes involved in creating electricity.
- Electromagnetism:
A key idea in producing electricity is electromagnetic induction. An electric charge flow is induced when a wire is moved through a magnetic field or when a magnetic field is shifted around a wire. In generators and alternators, this technique is used to transform mechanical energy into electrical energy. Large turbines are frequently used in power plants to rotate strong magnets inside coils of wire, producing an ongoing flow of electrons and energy.
- Chemical Reactions:
Electricity may also be generated through chemical reactions. One excellent illustration of this is batteries. A chemical interaction between several materials inside a battery releases electrons that may be caught and guided through a circuit to provide electrical power. In addition to being often utilised in automobiles and backup power systems, this kind of energy production is also widely employed in portable devices like smartphones and laptops.
- Thermal Power Plants:
Heat energy is converted into mechanical energy, which is subsequently converted into electricity in thermal power plants, such as coal, natural gas, and nuclear power plants. Coal or gas is used in fossil fuel power plants to heat water and create steam. High-pressure steam powers turbines that are connected to generators, which produce electricity from mechanical energy. Nuclear reactions are used in nuclear power plants to produce heat, which powers the turbines and creates electricity.
- Renewable Energy Sources:
In order to create power with the least amount of environmental damage, renewable energy sources including solar, wind, hydroelectric, and geothermal energy are increasingly used. The photovoltaic effect, in which photons from the sun displace electrons to create an electric current, is how solar panels turn sunlight into electricity.
Each of these methods contributes to the diverse portfolio of electricity generation, providing us with a reliable and sustainable source of power. By understanding the various processes involved in creating electricity, we can appreciate the complexity and innovation behind the systems that power our modern world.
For a deeper understanding of these concepts, we invite you to explore physics tuition at Miracle Learning Centre. Our experienced tutors are here to guide you through the intricacies of electricity generation, helping you grasp the fundamental principles and technologies involved. With our personalized approach to learning, we aim to ignite your curiosity and foster a solid foundation in physics.
How do we generate electricity?
Electricity is generated on a large scale in power plants using different methods. Here are some common techniques:
Turbines:
Turbines play a crucial role in generating electricity. By utilizing various fuel sources like coal, natural gas, or nuclear reactions, power plants produce steam. This high-pressure steam is directed onto turbine blades, causing them to spin. As the turbine rotates, it converts the kinetic energy of the steam into mechanical energy. The mechanical energy is then transformed into electrical energy using generators, where electromagnets and rotating coils create a flow of electrons.
Reciprocating Engines:
Reciprocating engines are commonly used in small-scale power generation or backup systems. These engines burn fuels like gasoline or diesel, creating an explosion that drives a piston back and forth. The reciprocating motion generates mechanical energy, which is then converted into electrical energy using a generator.
Photovoltaic Panels:
Photovoltaic (PV) panels, also known as solar panels, harness sunlight to generate electricity. When sunlight hits the PV panels, it excites electrons in the solar cells, creating a flow of electric charge. This direct current (DC) is converted into alternating current (AC) using inverters, making it suitable for powering homes and businesses. Solar power provides a clean and renewable source of electricity.
Let’s talk about the two forms that electricity may take, static or current, before going any farther. Static electricity is equally as vital to comprehend as current electricity since dealing with electronics will include it far more frequently.
Current Electricity:
Electric charge flowing continuously via a conductor is referred to as current electricity. The majority of the electrical gadgets and electronics we use on a daily basis are powered by it. End-users receive this form of electricity through electrical networks, which is produced by sources like power plants.
Electrons in current electricity travel via a closed-loop path, moving from a power source to a load and then returning to the source. It is characterized by an even, regulated flow of electric charge, allowing the dependable operation of many electrical systems.
Static Electricity:
When electric charges amass on an object’s surface, static electricity results. This frequently occurs when two objects with opposing charges touch each other or when specific materials are rubbed together, which causes electrons to transfer. Static electricity does not continually flow through a circuit like current electricity does.
Instead, it builds up on surfaces where it may be released by a spark or through touch. Static electricity may be seen in regular life in situations like when we are shocked after walking on carpet or when our hair stands up from friction. Static electricity has significant uses in sectors including printing, painting, and air purification, while being less frequently used for practical reasons.
What is Field?
In the context of electricity, a field refers to a region of influence or force around an object. It can exert forces on other objects within its vicinity. Fields can be visualized as invisible lines of influence, providing a framework to understand the behaviour of electric charges and their interactions.
What is an Electric Field?
A field in the context of electricity is the area around an item where its impact may be felt. It generates an unseen force that affects nearby items even when there isn’t a direct physical connection. An electric field, which forms when electric charges are present and present whether they are fixed or moving, is one such example. We may acquire insights into how charged particles interact and how electrical events happen by comprehending the idea of an electric field. It offers a framework for understanding the complex dynamics and actions of electricity in our environment.
When it comes to grasping the intricacies of electric fields and their applications, science tuition can be immensely beneficial. At Miracle Learning Centre in Singapore, we offer exceptional science tuition that provides comprehensive coverage of electric fields. Our experienced tutors employ interactive teaching methods to help students comprehend the complexities of this topic with ease. With the guidance and support of our science tuition, students can enhance their understanding of electric fields, develop strong conceptual foundations, and excel in their studies.
Electric Potential Energy:
Electric potential energy is a concept that revolves around the stored energy within a charged object in an electric field. When a charged object is positioned in an electric field, it possesses potential energy due to its interaction with the field. The amount of potential energy depends on the charge of the object and its position relative to other charged objects or the electric field.
This stored energy can be transformed into different forms, such as kinetic energy or light. For example, when a charged object is released in an electric field, its potential energy is converted into kinetic energy as it accelerates towards or away from other charges. Similarly, in electronic devices, electric potential energy is converted into light energy when electrons flow through a circuit and illuminate a bulb or power a screen.
Electricity in Action!
Electricity is not just a concept confined to textbooks and scientific experiments; it is an ever-present force that powers our daily lives. Imagine the flickering glow of streetlights illuminating the night, the hum of appliances bringing convenience to our homes, and the seamless operation of industries that drive our economy. These are just a few examples of electricity in action.
In our technologically advanced world, electricity enables us to communicate instantaneously across vast distances, navigate with precision using GPS systems, and access a world of information at our fingertips through the internet. From powering medical equipment that saves lives to fuelling transportation systems that connect us, electricity is the invisible force that keeps our modern society running smoothly. Its applications are endless, and as technology continues to evolve, so do the possibilities of harnessing electricity to drive innovation and progress.
Conclusion
Electricity is a captivating force that powers our world and fuels technological advancements. Understanding how it is created, generated, and harnessed allows us to appreciate its significance and leverage its potential. From the movement of electrons to the practical applications in our lives, electricity is an integral part of modern society. Through science tuition, such as that offered by Miracle Learning Centre in Singapore, you can enhance your knowledge and delve further into the fascinating realm of electricity. Embrace the electrifying journey of discovery and unlock the secrets of this remarkable form of energy.