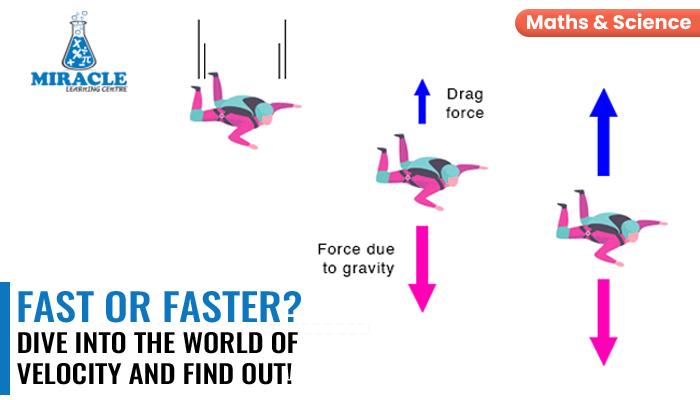
A cornerstone concept in the realm of physics is velocity, serves as a crucial metric for discerning the dynamic aspects of an object’s motion. This vector quantity encapsulates not only the speed at which an object is moving but also the direction in which it is heading. Velocity offers vital information regarding the complexities of motion, whether one is examining the space shuttle’s trajectory or an athlete’s acceleration. This exploration delves into the intricacies of velocity, including its units, types, and precise calculation methods. Come explore the basic ideas guiding object motion with us, and benefit from our expert Science tuition..
What is Velocity?
Velocity is the measure of an object’s displacement over time in a particular direction. Unlike speed, which is a scalar quantity representing only the magnitude of motion, velocity accounts for both speed and direction.
For example, a car traveling at 60 miles per hour to the east has a different velocity than a car traveling at the same speed to the west.
In mathematical terms, velocity (v) is defined as the change in displacement (Δx) divided by the change in time (Δt):
v =Δx/Δt
Units of Velocity:
The units of velocity are derived from the fundamental measurements of distance and time. In the International System of Units (SI), where the standard unit for distance is meters and for time is seconds, velocity is expressed in meters per second (m/s). This unit signifies the amount of distance an object covers in one second.
Other common units include kilometers per hour (km/h) and miles per hour (mph). The choice of units depends on the context and convenience of the given problem.
Types of Velocity:
Velocity can be further classified into various types based on its characteristics and the context in which it is used. Two primary types are initial velocity and final velocity.
Initial Velocity:
Initial velocity refers to the velocity of an object at the beginning of a particular time interval or motion. It is the speed and direction with which an object starts its journey. Initial velocity is a crucial parameter when analysing the motion of projectiles, vehicles, or any other moving object from a specific starting point.
Final Velocity:
Final velocity, on the other hand, is the velocity of an object at the end of a given time interval or motion. It signifies the speed and direction at the conclusion of an object’s journey. Calculating final velocity is essential for understanding the outcome of a moving object, such as determining the landing velocity of a projectile.
How to Find Velocity?
The process of finding velocity involves calculating both initial and final velocities, and the formulas for these calculations are derived from the fundamental equation of velocity:
Velocity(v)= Change in Time(Δt)/Change in Position(Δd)
Initial Velocity:
Determining the initial velocity (u) involves understanding the velocity of an object before any changes due to acceleration. The initial velocity can be calculated using the following formula:
u = v – at
where,
- u = initial velocity (m/s)
- v= final velocity (m/s)
- a = acceleration (m/s²)
- t = time between the start and end of the acceleration (s)
This formula provides a straightforward method for calculating the initial velocity of an object undergoing acceleration.
Final Velocity:
The final velocity of an object (v) is determined by adding its initial velocity (u) to the product of acceleration (a) and the time interval (Δt) it traveled. This relationship is expressed by the equation:
v = u + aΔt
Where:
- v is the final velocity
- u is the initial velocity
- a is the acceleration
- Δtis the change in time
This equation illustrates that the final velocity is the sum of the initial velocity and the product of acceleration and the change in time. In this context:
Δt= tv – tu
Here, (tv – tu) represents the time elapsed from the initial (u) to the final (v) states.
Therefore, for a given object, calculating its final velocity involves adding its initial velocity to the product of acceleration and the change in time, as indicated by the formula. Understanding this relationship provides valuable insights into how an object’s velocity evolves under the influence of acceleration over a specific time interval.
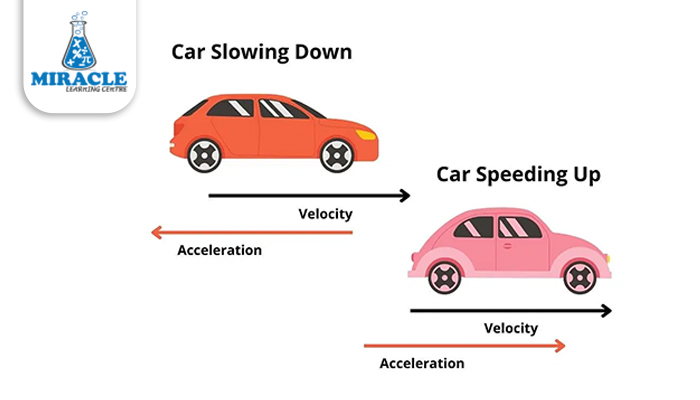
Speed and Velocity:
The terms speed and velocity often cause confusion due to their shared focus on the speed of motion. Despite their similarities, they diverge significantly. Speed solely indicates how fast an object moves, considering the distance covered.
In contrast, velocity not only gauges speed but also incorporates direction, denoting the object’s motion. Speed correlates with the distance travelled, while velocity corresponds to displacement.
Average velocity, calculated as total displacement divided by total time, is always less than or equal to average speed. This distinction arises from the fact that displacement cannot exceed distance, though the reverse is possible.
Difference between Speed and Velocity:
Now, let’s delve into a detailed comparison between speed and velocity, presented in a tabular format for clarity:
Speed–
- It is the quantitative measure of how quickly something is moving.
- It is primarily a scalar quantity.
- It is the rate of change of distance.
- The speed of an object moving can never be negative.
- Speed is a prime indicator of the rapidity of the object.
- Speed can be defined as the distance covered by an object in unit time.
Velocity –
- It defines the direction of the movement of the body or the object. |
- It is essentially a vector quantity.
- It is the rate of change of displacement.
- The velocity of a moving object can be zero.
- Velocity is the prime indicator of the position as well as the rapidity of the object.
- Velocity can be defined as the displacement of the object in unit time.
Get comprehensive knowledge about it with our science tuition:
For those seeking a deeper understanding of velocity and related physics concepts, enrolling in our science tuition program is a wise investment. Our science tuition in Singapore offers comprehensive lessons, practical examples, and hands-on experiments designed to solidify your grasp of velocity and its applications. Our experienced science tutors guide students through the intricacies of physics, making the subject more accessible and enjoyable.
In our science tuition program, students have the opportunity to explore real-world examples, engage in problem-solving exercises, and gain a holistic understanding of velocity and its significance in the broader field of physics. Whether you are a student aiming to excel in exams or an enthusiast eager to delve into the wonders of physics, our science tuition provides the support and resources you need. Our dedicated science tutors ensure a personalized learning experience, fostering a strong foundation in physics for academic success.
Conclusion:
In summary, velocity is a fundamental physics concept, capturing the rate of an object’s position change over time, considering both magnitude and direction. It is indispensable for analyzing and predicting object motion. Understanding velocity types, measurement units, and the distinction between speed and velocity provides a comprehensive insight into this critical physical parameter. Whether you’re a student tackling physics challenges or a science enthusiast, a strong understanding of velocity is pivotal. For in-depth comprehension and academic success, consider enrolling in a science tuition program to master the complexities of physics.